Today’s topic is Electrical Wiring Color Code Standards Malaysia. Obviously, you can find a great deal of Electrical Wire Colors-related content online. The proliferation of online platforms has streamlined our access to information.
There is a connection between the Electrical Wire Colors and Wire Color Code Plug information. more searching has to be done for Wire Color Code Plug, which will also be related to Wire Color Code Plug.

14 Reference List: Electrical Wiring Color Code Standards Malaysia | Wire Color Code Plug
- Electrical devices often use copper conductors because of their properties, including their high electrical conductivity, tensile strength, ductility, creep resistance, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion, solderability, resistance to electrical overloads, compatibility with electrical insulators, and ease of installation. Copper is used in many types of electrical wiring.[12][13] - Source: Internet
- Associated circuit protection, control, and distribution devices within a building’s wiring system are subject to voltage, current, and functional specifications. Wiring safety codes vary by locality, country, or region. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to harmonise wiring standards among member countries, but significant variations in design and installation requirements still exist. - Source: Internet
- Squirrels, rats, and other rodents may gnaw on unprotected wiring, causing fire and shock hazards.[17][18] This is especially true of PVC-insulated telephone and computer network cables. Several techniques have been developed to deter these pests, including insulation loaded with pepper dust.[citation needed] - Source: Internet
- Aluminium conductors are still heavily used for bulk power transmission, power distribution, and large feeder circuits with heavy current loads, due to the various advantages they offer over copper wiring. Aluminium conductors both cost and weigh less than copper conductors, so a much larger cross sectional area can be used for the same weight and price. This can compensate for the higher resistance and lower mechanical strength of aluminium, meaning the larger cross sectional area is needed to achieve comparable current capacity and other features. Aluminium conductors must be installed with compatible connectors and special care must be taken to ensure the contact surface does not oxidise. - Source: Internet
- In the United Kingdom, an early form of insulated cable,[19] introduced in 1896, consisted of two impregnated-paper-insulated conductors in an overall lead sheath. Joints were soldered, and special fittings were used for lamp holders and switches. These cables were similar to underground telegraph and telephone cables of the time. Paper-insulated cables proved unsuitable for interior wiring installations because very careful workmanship was required on the lead sheaths to ensure moisture did not affect the insulation. - Source: Internet
- For very large currents in generating stations or substations, where it is difficult to provide circuit protection, an isolated-phase bus is used. Each phase of the circuit is run in a separate grounded metal enclosure. The only fault possible is a phase-to-ground fault, since the enclosures are separated. This type of bus can be rated up to 50,000 amperes and up to hundreds of kilovolts (during normal service, not just for faults), but is not used for building wiring in the conventional sense. - Source: Internet
- Cable trays are used in industrial areas where many insulated cables are run together. Individual cables can exit the tray at any point, simplifying the wiring installation and reducing the labour cost for installing new cables. Power cables may have fittings in the tray to maintain clearance between the conductors, but small control wiring is often installed without any intentional spacing between cables. - Source: Internet
- The earliest standardized method of wiring in buildings, in common use in North America from about 1880 to the 1930s, was knob and tube (K&T) wiring: single conductors were run through cavities between the structural members in walls and ceilings, with ceramic tubes forming protective channels through joists and ceramic knobs attached to the structural members to provide air between the wire and the lumber and to support the wires. Since air was free to circulate over the wires, smaller conductors could be used than required in cables. By arranging wires on opposite sides of building structural members, some protection was afforded against short-circuits that can be caused by driving a nail into both conductors simultaneously. - Source: Internet
- In the United Kingdom, wiring installations are regulated by the Institution of Engineering and Technology Requirements for Electrical Installations: IEE Wiring Regulations, BS 7671: 2008, which are harmonised with IEC 60364. The 17th edition (issued in January 2008) included new sections for microgeneration and solar photovoltaic systems. The first edition was published in 1882. In 2018, the 18th edition of the wiring regulations BS7671:2018 was released and came into force in January 2019 and BS7671:2018 Amendment 1 was issued February 2020. BS 7671 is the standard to which the UK electrical industry adheres, and compliance with BS 7671 is now required by law through the Electricity, Safety, Quality and Continuity Regulations 2002. - Source: Internet
- Wiring systems in a single family home or duplex, for example, are simple, with relatively low power requirements, infrequent changes to the building structure and layout, usually with dry, moderate temperature and non-corrosive environmental conditions. In a light commercial environment, more frequent wiring changes can be expected, large apparatus may be installed and special conditions of heat or moisture may apply. Heavy industries have more demanding wiring requirements, such as very large currents and higher voltages, frequent changes of equipment layout, corrosive, or wet or explosive atmospheres. In facilities that handle flammable gases or liquids, special rules may govern the installation and wiring of electrical equipment in hazardous areas. - Source: Internet
- Aluminium wire was common in North American residential wiring from the late 1960s to mid-1970s due to the rising cost of copper. Because of its greater resistivity, aluminium wiring requires larger conductors than copper. For instance, instead of 14 AWG (American wire gauge) copper wire, aluminium wiring would need to be 12 AWG on a typical 15 ampere lighting circuit, though local building codes vary. - Source: Internet
- Where wiring, or raceways that hold the wiring, must traverse fire-resistance rated walls and floors, the openings are required by local building codes to be firestopped. In cases where safety-critical wiring must be kept operational during an accidental fire, fireproofing must be applied to maintain circuit integrity in a manner to comply with a product’s certification listing. The nature and thickness of any passive fire protection materials used in conjunction with wiring and raceways has a quantifiable impact upon the ampacity derating, because the thermal insulation properties needed for fire resistance also inhibit air cooling of power conductors. - Source: Internet
- The first rubber-insulated cables for US building wiring were introduced in 1922 with US patent 1458803, Burley, Harry & Rooney, Henry, “Insulated electric wire”, issued 1923-06-12, assigned to Boston Insulated Wire and Cable . These were two or more solid copper electrical wires with rubber insulation, plus woven cotton cloth over each conductor for protection of the insulation, with an overall woven jacket, usually impregnated with tar as a protection from moisture. Waxed paper was used as a filler and separator. - Source: Internet
- Some terminations on wiring devices designed only for copper wire would overheat under heavy current load and cause fires when used with aluminium conductors. Revised standards for wire materials and wiring devices (such as the CO/ALR “copper-aluminium-revised” designation) were developed to reduce these problems. While larger sizes are still used to feed power to electrical panels and large devices, aluminium wiring for residential use has acquired a poor reputation and has fallen out of favour. - Source: Internet
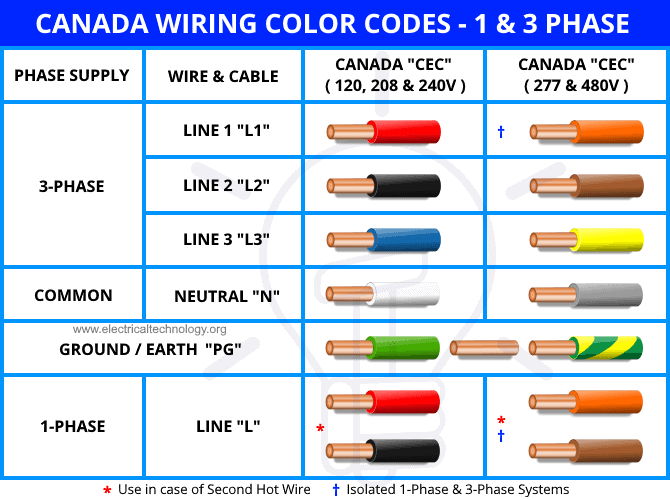 Following are some suggestions on where to begin your search for data on Live Wire Color Code:
You should try to find 3 Phase Wire Color Code-related information from reputable places. Libraries, online resources, and even paid journalists all fall under this category.
Following are some suggestions on where to begin your search for data on Live Wire Color Code:
You should try to find 3 Phase Wire Color Code-related information from reputable places. Libraries, online resources, and even paid journalists all fall under this category.It’s crucial to be aware of the many electronic media sources available when researching Wire Color Code Plug, such as Google and YouTube. You may also get info about Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia on social media sites like Facebook and Twitter.
Video | Electrical Wiring Color Code Standards Malaysia
It’s crucial to read to examine the authenticity of each source in order to acquire the greatest information regarding Wire Color Code Plug. You’ll learn more about Neutral Wire Colour Malaysia after watching the films included in this post, which come from a variety of different sources. Information on a wide range of topics may be easily accessed via the internet.
## Notable features of Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia include:- Electrical Wiring Color Code Standards Malaysia
- Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia
- Live Wire Color Code
- Electrical Wire Colors
- 3 Phase Wire Color Code

Because there are so many websites and forums that provide information about Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia, it should not be difficult for you to locate the data that you want.
The majority of individuals are accustomed to taking a completely different approach when it comes to obtaining information regarding Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia. This makes it possible to take a more in-depth look at the information that is available about electrical wiring color code standards malaysia and how it might be utilized.

methods for producing information displays about Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia that are both aesthetically pleasing and functional. In commercial and marketing settings, as well as for the purpose of conveying information on Live Wire Color Code, they are useful tools to have. Because of this, we also supply some photographs relating to 3-Pin Plug Wire Colours In Malaysia.
In summing up, I’d like to say that this article offers a general summary of Electrical wiring. Also covered are Neutral Wire Colour Malaysia and Electrical Wiring System In Malaysia, which serve as a benchmark for evaluating the depth of your understanding of Live Wire Color Code.